Introduction – Should You Turn On Emergency Heat
Heat pumps are an energy-efficient alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems, offering both comfort and cost savings for homeowners. One important feature of heat pumps is the emergency heat setting, which can be critical during extremely cold temperatures or when the heat pump is not functioning properly. In this article, we’ll explore what emergency heat is, why it exists, when to use it, what to do if it doesn’t work, and some top brands offering heat pumps with this essential feature.
What is Emergency Heat?
Emergency heat, also known as auxiliary heat or backup heat, is a setting on heat pumps that activates a secondary heating source when the heat pump cannot provide adequate heating. This secondary source is typically an electric resistance heater or a gas furnace, which provides additional heat to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. The purpose of emergency heat is to ensure that your home remains warm during extreme cold or when the primary heating system is not working effectively.
Why Emergency Heat Exists
The emergency heat setting exists for several reasons. First, it provides protection against extremely low outdoor temperatures, which can cause a heat pump to lose efficiency and struggle to maintain the desired indoor temperature. Second, it serves as a backup option in case the heat pump malfunctions or fails to provide enough heat due to issues such as ice buildup on the outdoor unit or mechanical failure. Lastly, using emergency heat can help preserve the efficiency and longevity of the heat pump by reducing the strain on the system during extreme conditions.
When Should You Switch Your Heat Pump To Emergency Heat
Emergency heat should be activated in specific scenarios. If the outdoor temperature drops to a level where your heat pump cannot efficiently extract heat from the air, it may be necessary to use emergency heat. Additionally, if your heat pump is malfunctioning or failing to provide enough heat, switching to emergency heat can help maintain a comfortable indoor temperature until the issue is resolved. In both cases, it’s essential to consult with an HVAC professional to diagnose and address the underlying problems.
What Happens If Emergency Heat Doesn’t Work
If your emergency heat setting doesn’t work, there may be several potential causes, such as a blown fuse, tripped circuit breaker, or issues with the wiring or thermostat. To troubleshoot the problem, check your thermostat settings, inspect your circuit breakers and fuses, and consult your heat pump’s owner’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps. If you’re unable to resolve the issue, it’s best to seek professional help from an HVAC technician to diagnose and repair the problem.
Top Brands
- Trane: Trane is a leading HVAC brand known for its high-quality and reliable heating and cooling products. Many of their heat pump models come equipped with emergency heat settings, such as the Trane XV20i and XR16, which offer homeowners peace of mind and additional heating support during extreme weather conditions.
- Carrier: Carrier is another top HVAC brand offering heat pumps with emergency heat settings. Known for their innovative and energy-efficient products, Carrier heat pumps like the Infinity 20 and Performance 15 provide homeowners with reliable backup heating options when needed.
Switching To Emergency Heat Incurs Higher Costs
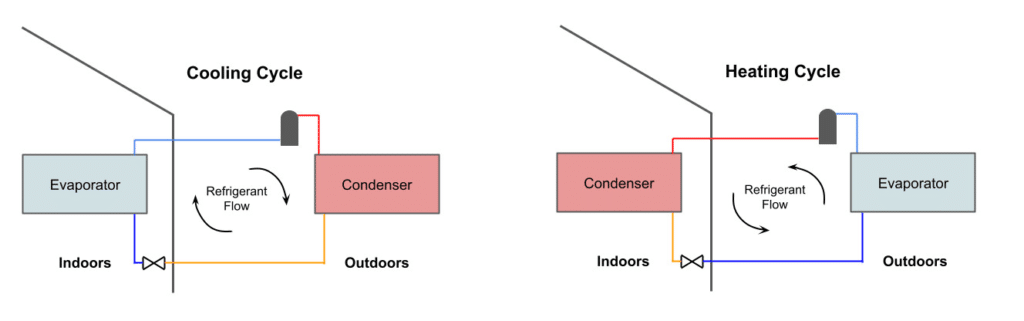
Heat pumps and electric resistance heaters are two common options for heating homes, but they differ significantly in terms of efficiency. A heat pump is a type of HVAC system that uses refrigerant and a compressor to transfer heat from one place to another, extracting heat from the outdoor air and releasing it indoors to warm the living space. In contrast, an electric resistance heater generates heat by passing an electric current through a conductive material, such as metal coils, which in turn warms the surrounding air.
The efficiency of a heat pump can be significantly higher than that of an electric resistance heater due to the way they generate heat. While electric resistance heaters convert almost all of the electrical energy they consume into heat, they are considered less efficient because they must generate all of the heat they provide. On the other hand, heat pumps merely transfer existing heat from one location to another, requiring less energy input to achieve the same level of heating output. This ability to move heat rather than generate it from scratch makes heat pumps considerably more energy-efficient than electric resistance heaters.
It’s important to note that the efficiency of a heat pump can vary depending on factors such as outdoor temperature and system performance. When outdoor temperatures are mild, heat pumps can operate at efficiencies of 200% to 300%, meaning they can provide two to three times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume.
The standard technical term for heat pump efficiency is Coefficient of Performance (COP). The COP is a ratio that measures the amount of heat energy a heat pump can produce compared to the electrical energy it consumes. A COP of 2 to 3 means that the heat pump can produce 2 to 3 times more heat energy than the electrical energy it uses, which translates to an efficiency of 200% to 300%.
However, as temperatures drop, the efficiency of the heat pump can decrease, as it becomes more challenging to extract heat from the cold outdoor air. In extreme cold conditions, the efficiency of a heat pump may be similar to that of an electric resistance heater.
The main advantage of heat pumps over electric resistance heaters lies in their operational costs. Since heat pumps are more energy-efficient, they consume less electricity to produce the same amount of heat, resulting in lower energy bills. Depending on the climate and usage patterns, homeowners who switch from electric resistance heaters to heat pumps may see significant savings on their monthly heating bills.
Conclusion
Understanding the purpose and function of emergency heat in heat pumps is crucial for homeowners who want to maintain comfort and efficiency during extreme weather conditions. By choosing a heat pump system with an emergency heat setting from reputable brands like Trane or Carrier, you can ensure that your home stays warm even when the primary heating system struggles. Additionally, regular maintenance and consultation with HVAC professionals can help keep your heat pump running efficiently and effectively, maximizing comfort and energy savings throughout the year.
