Introduction – CAFO Sustainability
CAFO stands for Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations and are agricultural facilities where a large number of livestock are kept and raised in confined spaces. No doubt, these facilities are an integral part of modern industrialized agriculture because without them we would not achieve the current level of production efficiency and ability to feed so many people.
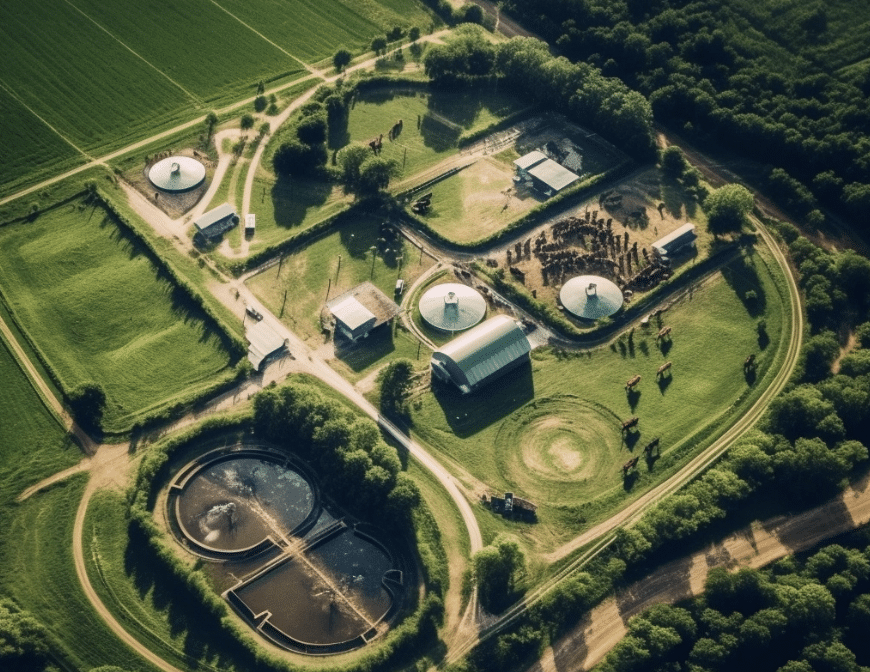
But at the same time, CAFOs are becoming an increasingly significant topic of discussion in the realm of environmental sustainability and carbon reduction. This article will delve into the regulations, policies, and industry trends shaping the future of CAFOs while outlining practices and strategies for a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach in the industry.
Environmental Impacts and Sustainable Solutions
CAFOs have been linked to a variety of ecological disturbances, including greenhouse gas emissions and negative impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. Let’s take a look at a list of them.
- Water Pollution: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) identifies CAFOs as a primary source of nutrient pollution in waterways. According to the Natural Resources Defense Council, the waste produced by a typical CAFO with 800,000 pigs produces more than 1.6 million tons of waste a year, which is one-and-a-half times more than is produced by the city of Philadelphia. When improperly managed, these nutrients can enter waterways and contribute to harmful algal blooms and dead zones.
- Air Pollution: CAFOs release a variety of pollutants into the air, including methane, nitrous oxide, and ammonia. According to a 2013 report by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, one dairy farm with 2,500 cows produces as much waste as a city of 411,000 people, leading to significant amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Exposure to these pollutants can cause health problems for local residents, including respiratory issues and other diseases.
- Antibiotic Resistance: The Union of Concerned Scientists estimates that around 70% of all antibiotics produced in the U.S. are used in livestock, often as growth promoters or to prevent disease in crowded conditions. This can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which can pose a major threat to human health.
- Animal Welfare: There’s growing concern among consumers and animal rights advocates about the conditions in which animals are kept in CAFOs. The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) estimates that 99% of farm animals in the U.S. are raised in CAFOs. These animals often live in close confinement, with limited access to the outdoors or opportunities for natural behavior.
- Worker Health and Safety: According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), workers in CAFOs may be exposed to a variety of occupational hazards, including injuries, respiratory exposure to animal waste, and zoonotic infections (infections transmitted from animals to humans). These risks are a significant concern for the wellbeing of workers.
- Climate Change: According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, livestock accounts for 14.5% of all human-induced greenhouse gas emissions, with the majority of these emissions coming from large-scale, intensive farming operations like CAFOs.
By initiating sustainable and eco-friendly practices, the industry can mitigate its environmental footprint. Many CAFOs have begun to invest in waste-to-energy projects, converting animal waste into biogas for energy or compost for agricultural use. Furthermore, adaptation strategies for climate-smart agriculture and effective land management practices can help reduce carbon emissions and protect biodiversity. Reforestation and afforestation efforts around CAFO sites are important contributors to carbon sequestration and the restoration of natural habitats.
CAFO Regulations and Policies for Sustainability
As governmental bodies recognize the environmental consequences linked to CAFOs, new regulations and policies are being implemented, with more anticipated changes on the horizon by 2023. Current regulations focus on limiting emissions, reducing carbon footprints, and enforcing responsible waste management practices. Upcoming regulations are expected to encourage a transition to renewable energy sources and promote circular economy principles.
Climate change adaptation strategies will become increasingly crucial, as CAFOs are expected to face more stringent regulations concerning carbon emissions and waste management. Encouraging access to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is aimed at reducing dependency on fossil fuels while lowering emissions.
Recent Changes In CAFO-Related Laws

There have been numerous pieces of legislation at various levels of government in the United States pertaining to CAFOs. These have addressed issues such as waste management, water and air quality, animal welfare, and public health.
For instance, on the federal level, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates CAFOs under the Clean Water Act’s National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permitting program. This program has undergone various changes and adjustments over the years to address ongoing issues related to CAFOs.
Additionally, states have their own regulations that often work in tandem with federal regulations. For example, North Carolina, a state with a high concentration of CAFOs, enacted a moratorium on new swine CAFOs in 1997, and this was made permanent in 2007.
There has been a broader trend towards increased regulation and oversight of CAFOs due to growing awareness of their environmental and public health impacts.
Sustainable Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
As consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly and ethically produced foods, the CAFO industry has seen increased demand for sustainable and responsibly sourced animal products. This trend has led to various carbon reduction initiatives and sustainability measures throughout the industry, such as adopting renewable energy sources, investing in new technologies, and collaborating with environmental organizations.
In the same vein, alternative protein sources such as algal protein, soy protein and imitation meats are gaining popularity. This shift is expected to influence the industry’s commitment to sustainability and carbon reduction.
Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable CAFOs
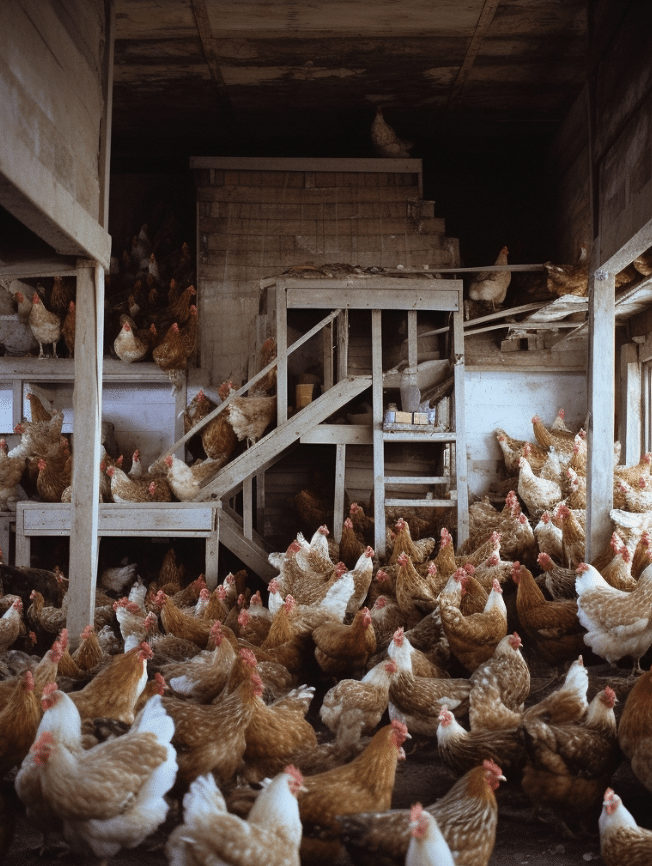

Achieving a balance between productivity and environmental preservation presents a significant challenge for the CAFO industry. Meeting carbon reduction goals while maintaining competitiveness in the market will require continuous innovation in clean technology, eco-friendly infrastructure, and the establishment of public-private partnerships to support sustainable solutions.
Individual consumers also play a critical role in shaping the future of the CAFO industry. By making conscious choices to support local producers, consume responsibly, and adopt more plant-based diets, consumers can contribute to reduced carbon emissions and drive the demand for more sustainable business practices within the industry.
Conclusion – CAFO
Understanding and addressing the challenges faced by CAFOs is vital as we approach 2023 and strive for a more sustainable future. As regulations, industry trends, and consumer preferences evolve, the emphasis on carbon reduction and eco-conscious initiatives will continue to grow. By encouraging dialogue, innovation, and advocacy for sustainable practices, both industry players and consumers can work together to ensure the future of CAFOs aligns with the goals of environmental preservation and reduced carbon emissions.
