
Five years ago I bought my first LED light bulbs. They were to replace halogens in my bathroom. I spent too much money on not enough lumens and way too many kelvin. You know what I mean?
No? Perfect. Let’s make a deal?!
If you spend ten minutes reading this post I promise you that by the end of it you’ll understand how to buy a low energy light bulb. In return I’ll try not to bore you senseless.
Ready? Let’s do this. With five simple questions.
1) What Fitting Do You Need?
This is simple, but you really don’t want to mess it up.
Although there are literally hundreds of light fittings in existence, your home probably only has a couple. I’ve got two in my ceiling fittings, a couple more in table lamps. In the image below there are some common ones for the UK and US.
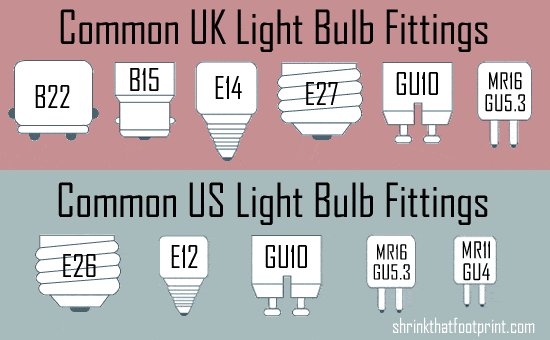
‘B’ is for Bayonett, it’s a bit of a British Empire thing. ’E’ is for Edison Screw, dominant in the US thanks to Thomas. ’GU’ is for, gee you really need to get yourself a life a if you know what ‘GU’ means.
You don’t need to know what they mean. But if you scribble down the fittings before you start shopping for bulbs not only will they fit, they’ll be the right voltage too.
2) What Shape Bulb Do You Want?
Bulb shape is not just a question of liking the look of a bulb, it is about how it throws light. The design of the bulb determines what direction the light goes, so you need to consider what you want the bulb to do.
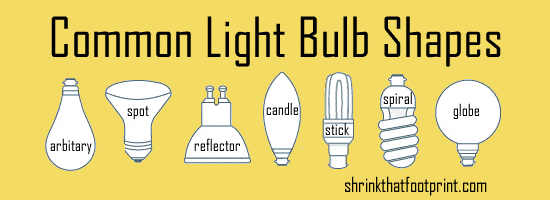
There is literally an alphabet describing different bulb shapes, but since I promised not to bore you I’m just not going to go there. All you need to do for shape is use your common sense.
For a ceiling pendent you might want an ‘omnidirectional’ bulb like the arbitary, stick or spiral shape. For a lamp you might need a candle shape with a broad spread. And if you are putting a spot into a recessed downlight you’ll need a reflector with an appropriate beam width for the context.
A bulb that throws the wrong angle light can be really annoying, so do take the time to contemplate the shape before you buy.
3) How Bright Does It Need To Be?
It is no longer enough to think about bulb brightness in terms of watts. That was fine when we only had incandescents, but now we need to start thinking in lumens.
This is particularly the case when buying LEDs, because the use of the term ‘replacement’ is can be abused by bulb re-sellers, and occasionally by lesser manufacturers too. The following tables are a rough explanation of how many lumens you get from your watts for different bulb technologies for a standard fitting.
Now I’m very sorry to do this, but I had to make two charts to explain this properly. One for our readers in the low voltage (120V) countries like the US, Canada, Brazil and Japan. And a second one for readers in high voltage (240V) countries, that’s the rest of the world.
The American Lumen:
If you live in the US, or anywhere else with a lower voltage grid, please look at this first chart. If you live elsewhere skip straight to the second.
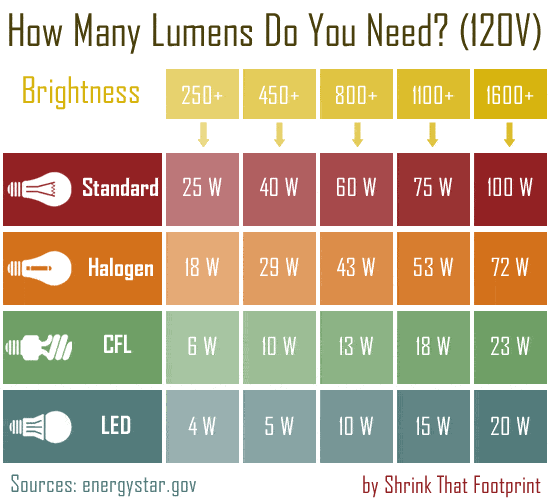
At the top of this chart you have the brightness of the bulb in lumens. This is the number you need to start thinking in.
Let’s say you’re in the US and want to replace an old 60W bulb and get a similar amount of light. Then you know you’ll need to get at least 800 lumens in order to match the brightness of the old 60W. Sometimes manufacturers will compare a bulb to an old “standard” one, for example put on the packaging “equivalent to 60 W incandescent”. That’s a way for old-timers to figure out what power requirements.
Notice that LEDs are super efficient, CFLs not far behind, and Halogens and Standard (incandescent) are the worst.
Got it? If you know your lumens, you won’t be mis-sold a ‘replacement bulb’ that isn’t bright enough.
The High Voltage Lumen (UK):
In the rest of the world grids have higher voltage, meaning that lumen equivalent for standard incandescents is different.
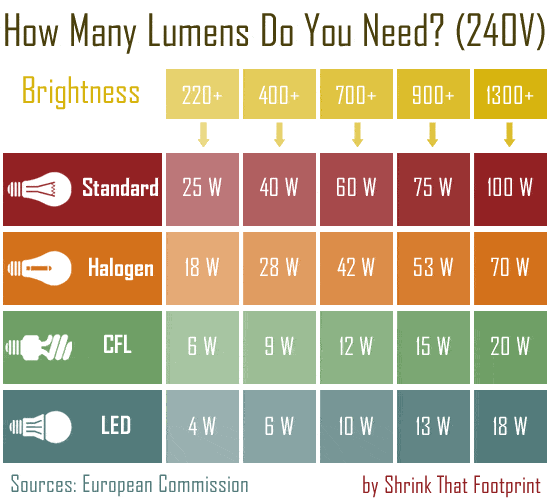
At the top of this chart you have the brightness of the bulb in lumens. This is the number you need to start thinking in.
Let’s say you’re in the UK and want to replace an old 60W bulb and get a similar amount of light. Then you know you’ll need to get at least 700 lumens to get a similar brightness to the old bulb.
Knowing your lumens means you will get the brightness you want, and avoid being mis-sold ‘replacement bulbs’.
A quick word on spotlights:
Just spot me a second here. Both the two charts above are designed to help you replace a normal lightbulb. When it comes to spotlights you can often experiment with going for fewer lumens. In our bathrooms I have replaced 700lm halogens with 320lm LEDs and actually prefer the light. The result is a 90% energy use reduction per bulb.
4) Do You Want Warm Or Cold Light?
This question might sound complicated, but it is dead easy and one of the great things about LEDs.
The temperature of light can be measured in terms of ‘Kelvin’. Very orange light has a low number of Kelvin, for example a candle is about 1,500K. Daylight is much colder, often above 5,000K. Here is the scale.
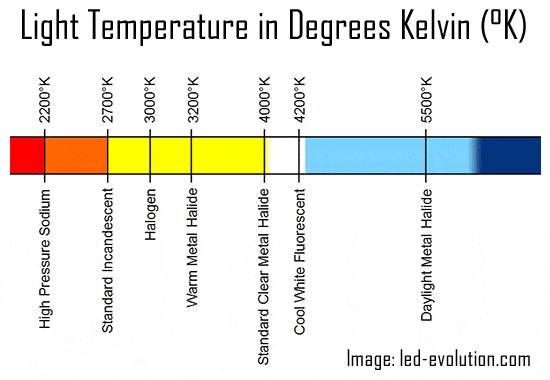
Kelvin – an aside into physics
The Kelvin is a pretty obscure way to measure the color of light, but its nice because it all fits on a single scale. The history of the Kelvin is from theoretical physics, a branch of it called statistical mechanics. In that theory are idealized constructs called “Black Body Radiators” – a bit like the spherical cows that mathematicians and physicists use to illustrate basic points about physics. A black body radiator acquires its color by virtue of its heat energy. For example, at 2700 Kelvin, which is about 4400 Fahrenheit, very very hot – the black body radiator is so hot that it has this yellowish color. This is where the Kelvin to color relationship comes from.
It turns out that the tungsten filament inside an incandescent bulb does in fact heat up to about 3000-4000 Fahrenheit, the reason why it acquires that yellowish, warm white color.
Interpreting the Kelvin color scale
When it comes to household light bulbs the temperature choices are very simple. Most people simply want what is called ‘warm white’ (2,700k) to replicate the warm, slightly yellow glow of an old incandescent or halogen.
In a kitchen, bathroom or other situations you may prefer a slightly less yellow light, sometimes called a natural white (3,000K). You may want to try cool white (4,000K). Or for a very specific style (5,000K). Anything above that starts to get a little blue.
This type of temperature choice is mostly associated with LEDs. If your home has a quite modern style you should definitely consider trying some cooler temperatures, as they can look great in the right context.
5) Are LEDs Good Value Yet?
Compact fluorescent (CFLs) bulbs are now so cheap that a CFL can pay itself off with energy savings in just months for a well used bulb. I personally quite like CFLs in the right context, but if you want instant light, dimming or cooler light they aren’t great.
LEDs on the other hand are gradually overcoming many of these problems. The main issue with LEDs at this point is their upfront cost. This is particularly true for 75W and 100W replacements (I’m waiting for prices to drop).
With this in mind let’s crunch some numbers and see how the payback is for LEDs. In the following chart I estimate how quickly energy savings will recoup the cost of replacing a 60W incandescent with a 10W LED that costs $10, assuming the bulb is used for 2 hours each day.
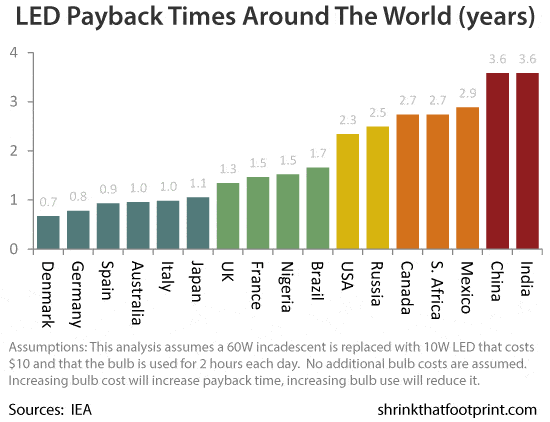
Because of the huge difference in the prices of electricity the $10 outlay for the LED pays itself off in anything from 9 months in expensive Denmark to three and a half years in India or China, where electricity is cheap.
Of course a 60W LED for $10 is still quite cheap. If it costs you $20 to get such a bulb you’d need to double these numbers. On the other hand if you are using the bulb 4 hours a day, then you should halve them. What does this mean for you in practical terms?
- Cheaper LEDs payback faster
- Payback is faster where electricity is expensive
- The more you use a bulb the faster the payback
- Replacing CFLs with LEDs is not yet cost effective
In most cases the one year running cost of an incandescent bulb you use regularly (>2 hours a day) is greater than any drop in LED prices we are likely to see. So it makes sense to switch when you see a decent value bulb. However, if you don’t use a bulb much (< 1 hour a day) you may want to wait for falling prices. Especially in the 100W replacement range which are still extortionate.
I have one incandescent left in my loft that I’d be lucky to use for 10 hours a year. I’ll probably only switch it if it blows. On the other hand, LEDs are notoriously long lasting because they don’t “burn out” in the same way.
6. Home Automation Integration
When choosing LED bulbs for your home, one important consideration is the home automation protocol and technology compatibility. Smart LED bulbs that integrate with home automation systems like Zigbee, Z-Wave, or Wi-Fi can offer enhanced functionality, such as remote control, scheduling, and integration with other smart devices for a comprehensive home automation experience.
6 Steps To Buying An Energy Saving Light Bulb
If you’ve made it this far you now know a lot about light bulbs. Because I promised not to bore you I’ve decided not to discuss dimming (read the labels), color rendering (above 80 please) and bulb lifespan (buy a known brand).
Let’s just recap the five steps:
- Fitting: Write down the code
- Shape: Decide on the best shape
- Brightness: Get enough lumens!
- Temperature: Warm or cool?
- Cost: Look for good value bulbs
- Home Automation Integration: Consider the protocols compatible with the bulb
Like I said in the introduction, I bought my first LED five years ago and only really got the first of these five steps correct. But things have changed an awful lot in five years, and LEDs are now becoming a really sensible option. CFLs remain excellent value due to their low prices and running costs, but you can’t always get the light you want.
If you have never bought LEDs before I highly recommend trialing a single bulb, or spotlight, first before buying too many. LEDs are not cheap and last a long time, so you want to be sure about fitting, shape, lumens and kelvins before going all in on them. I also recommend looking for specials on known brands or having a money back guarantee up your sleeve.
Here in the UK I’m on the lookout for decent 10W LEDs around the £10 mark. This Verbatim LED 10,5 W verbatim is a great deal for £9.99. Or something like this 10 Watt LED (or in a screw fit). I’ve just bought this Philips Master because I’ve always liked the look of it and saw a big price drop . For bathroom or kitchen spots I prefer LEDHUT.
Looking over the pond to the US I’m almost jealous. You guys get similar 10W LEDs for $10. This great 11W LED Dimmable from Phillips (complete with Energy Star rating) for $15. Interesting slim style bulbs. Your LED spots are cheaper too. And you can buy remote controlled color changing LEDs for just $13, which is not boring!!
If you made it the end, thanks for reading. I wish you much success with your LED hunt and hope you get the right fit, shape, brightness and temperature at a decent price. Most importantly I hope you prefer the light of your new bulb, as that is the main test of success. This post is one of the efficiency projects connected to our How to Save Money on Electricity video program. If you enjoyed it you should go check it out.
Lindsay Wilson
I founded Shrink That Footprint in November 2012, after a long period of research. For many years I have calculated, studied and worked with carbon footprints, and Shrink That Footprint is that interest come to life.
I have an Economics degree from UCL, have previously worked as an energy efficiency analyst at BNEF and continue to work as a strategy consultant at Maneas. I have consulted to numerous clients in energy and finance, as well as the World Economic Forum.
When I’m not crunching carbon footprints you’ll often find me helping my two year old son tend to the tomatoes, salad and peppers growing in our upcycled greenhouse.
