Introduction – Grid Infrastructure
Have you ever wondered about the science of electricity transmission? Electric transmission towers are the infrastructure of the electric power industry, and they play a very important role in ensuring the safe and stable operation of the power grid. As one of the most important parts of the power grid, transmission towers are generally designed and constructed by professional power transmission tower manufacturers.
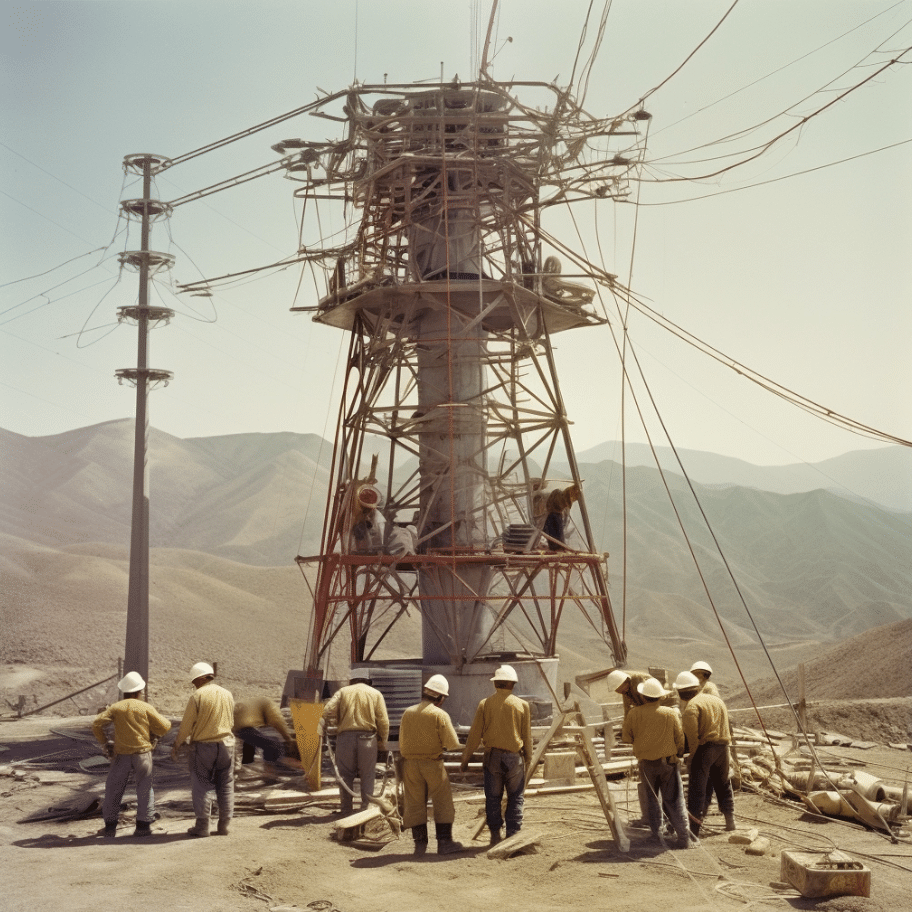
In the past, most transmission towers were made of steel, but in recent years, more and more transmission towers have been made of concrete.
The main reason for this change is that concrete transmission towers are more resistant to weathering and corrosion than steel transmission towers and have a longer lifespan.
In addition, concrete transmission towers are also much easier to construct than steel ones, which can save a lot of time and money.
There are many different types of transmission towers in use worldwide, and the specific type of transmission tower used in a particular area depends on a number of factors, such as the climate, the terrain, and the voltage of the power grid.
What is a Transmission Tower?
A transmission tower is a tall structure used to support high-voltage electrical power lines. Transmission towers are usually made of steel and can be freestanding or guyed. The tallest transmission towers in the world are over 2,000 feet tall.
Transmission towers are necessary because they help to keep power lines from sagging or touching the ground. This prevents outages and keeps the electricity flowing smoothly.

Transmission towers come in various shapes and sizes and are designed to meet the specific needs of the power lines they support. The tower type depends on the power line’s voltage, the conductor’s weight, and the terrain.
Some transmission towers are even designed to be camouflaged so that they blend in with their surroundings. They are also known as powerline towers or electricity pylons.
Impact On Your Life – Delivery Charges On Your Electric Bill
Think that towers are abstract and really have no effect on your life? Take a look at your electric bill next time. You will find the cost of electricity and then “delivery charges”.
This refers to the transport of electricity from the source to your home. The cost of building, maintaining, and operating the transmission network (including transmission towers and power lines) is factored into the price that consumers pay for electricity. This is usually included in the transmission and distribution charges on your electric bill.
The exact proportion of your bill dedicated to delivery and transmission can vary depending on your location and the specific practices of your utility company, but it’s not uncommon for these charges to constitute anywhere between 20% to 50% of your total bill.
These costs cover the maintenance and operation of transmission towers, power lines, substations, and other necessary infrastructure for delivering electricity.
Transmission Tower And Lines: Damage And Repair
Transmission lines and towers can suffer damage due to a variety of factors, including environmental challenges and physical impacts. Severe weather conditions like storms, high winds, and ice buildup are common culprits, with ice, in particular, causing structural stress due to increased load.
Corrosion, especially in steel towers, and natural disasters such as earthquakes and floods also pose significant risks. Mechanical impacts, such as vehicle collisions, can directly damage structures, sometimes shearing off tower legs.
The repair process includes replacing damaged components, cleaning insulators, tightening joints, and checking the foundation of towers. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent flash-overs and ensure efficient power transmission.
Live line maintenance, where repairs are conducted without power isolation, is used for critical loads to avoid disrupting power transmission. This method is applicable for all voltage levels from low to ultra-high.
Repairing transmission towers can be complex and often requires innovative solutions. For instance, Great River Energy faced challenges with ice buildup and damage from tractors, necessitating unique repair strategies. Ice buildup, particularly rime ice, can significantly enlarge the conductor’s diameter, leading to structural failures.
Electric Transmission Tower Parts
There are many different types of electric transmission towers. The most common type is the steel lattice tower. Steel lattice towers are made up of steel poles that are interconnected with each other to form a lattice. These towers are very strong and can support a large amount of weight.
Another type of electric transmission tower is the guyed mast. Guyed masts are made up of a single pole supported by guy wires.
These towers are not as strong as steel lattice towers, but they can be much taller. The third type of electric transmission tower is the tubular steel pole. Tubular steel poles are made up of a series of connected tubes.
These poles are very strong but not as tall as guyed masts. Electric transmission towers play an important role in the electrical grid. They help to support power lines and keep them from falling. Electric transmission towers come in all shapes and sizes, each with a unique function.
Types of Electrical Transmission Towers
A full-scale utility grid has three towers: transmission, distribution, and subtransmission.
Transmission Towers
The purpose of transmission towers is to support high-voltage power lines that carry electricity over long distances. These towers are typically made of steel and can be either lattice or tubular.
The most common type of transmission tower in the United States is the Angle Structure, which has diagonal bracing that gives it a triangular shape.
Distribution Towers
On the other hand, distribution towers support lower-voltage power lines that distribute electricity to homes and businesses within a relatively small area. These towers are typically made from wood or metal and are much shorter than transmission towers.
The most common type of distribution tower in the United States is the H-Frame, which has two vertical supports connected by a horizontal cross member.
Subtransmission towers
Subtransmission towers are similar to distribution towers in that they are used to support lower-voltage power lines; however, subtransmission lines carry electricity over longer distances than distribution lines.
As such, subtransmission towers tend to be taller than distribution towers but shorter than transmission towers. The most common type of subtransmission tower in the United States is the monopole, which has single vertical support.
Each type of electrical transmission tower serves a specific purpose and is designed accordingly. Understanding the different types of transmission towers is essential for ensuring any electrical grid’s safe and efficient operation.

What Is The Science Behind Electric Transmission Lines?
According to How Stuff Works, “An electric transmission line is a high-voltage wire that carries electricity from generation plants to substations.” The lines are composed of the conductor, the insulator, and the ground wire.
The conductor is usually made of copper or aluminum and is responsible for carrying the electric current. The ground wire helps to stabilize the voltage and prevents outages. The insulator is made of ceramic or plastic, protecting the conductor from damage.
Transmission lines are typically supported by towers or pylons, which help to keep the line taunt and prevent it from sagging. Transmission lines must be regularly maintained and repaired to function properly.
Over time, exposure to weather and other elements can cause damage to the lines, which can lead to outages and other problems. As a result, regular maintenance is essential to keeping the power grid running smoothly.
Are Transmission Towers AC or DC – Shadow of the Edison vs Tesla Wars
The answer might surprise you. Most transmission towers are, in fact, AC, not DC. This is because AC is much more efficient than DC when transmitting electricity over long distances. DC requires a higher voltage to travel the same distance as AC, which means more energy is lost during transmission.
In fact this was one of the great public battles between two great inventors Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla. Edison was a proponent of his DC system and worked hard to discredit Tesla’s AC system. Many years later, we are using Nikola Tesla’s ideas for long range transmission.
Part of the reason for the shift to AC is because AC can be easily converted to DC using a transformer, while the reverse is not true.
For these reasons, AC is the preferred choice for most transmission applications. However, there are some exceptions. DC is sometimes used for short-distance transmission or in cases where a very high voltage is required.
In these instances, DC can provide certain advantages over AC. Ultimately, whether to use AC or DC for transmission depends on various factors, including the specific application and the desired outcome.
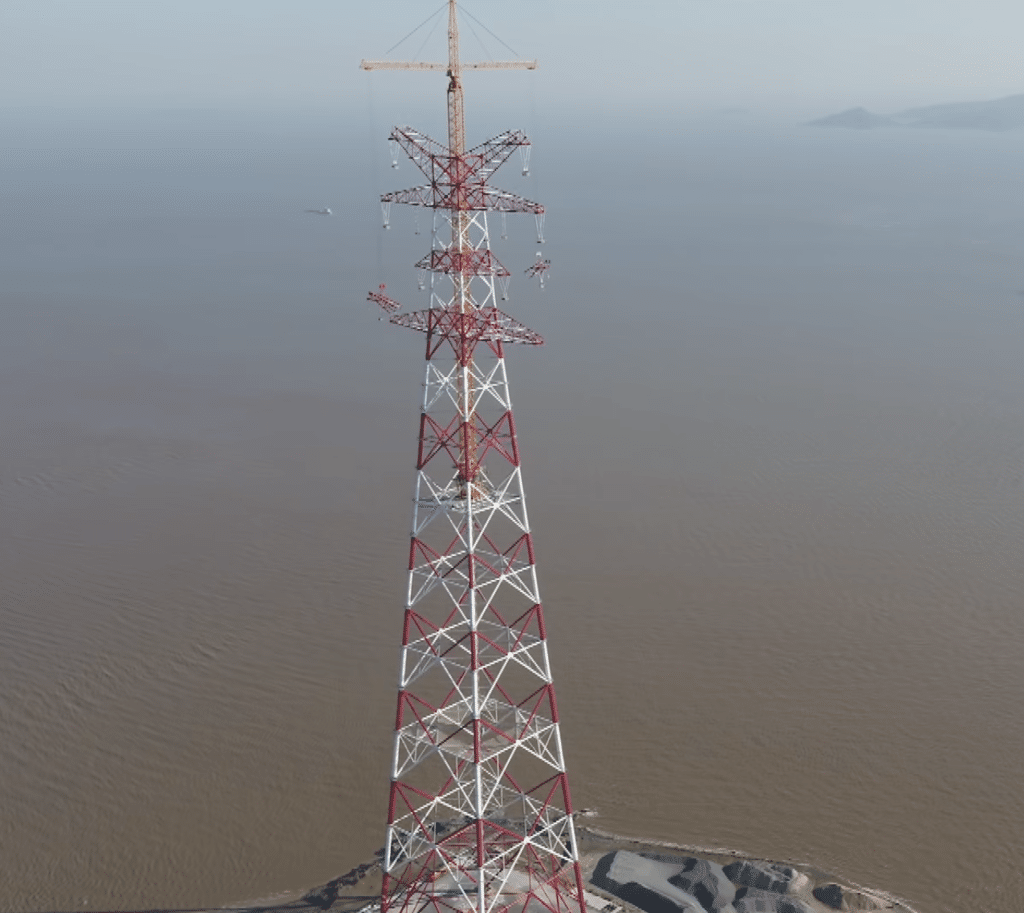
The Largest Transmission Tower In The World
The country of China has invested heavily in infrastructure in the recent decade, seeing the tallest electric transmission tower put into operation in the province of Zhejiang.
The tower is 380m high, which dictates the width of the span to be crossed by the wires, in turn mediated by the droop of the catenary and the strength of the cables. The total weight is a whopping 7,000 tonnes and is needed for carrying the very large 500,000 volts across such a long span of water.

Wrapping Up
In conclusion, transmission towers are an essential part of the electrical grid. There are three main types of transmission towers: angle structures, distribution towers, and subtransmission towers. Each type of tower serves a specific purpose and is designed accordingly.
